Migraine Burden
Migraine is a major global health issue that affects over 10% of the population (≈ 1 billion people globally) and is the second leading cause of years lived with disability worldwide.1 In the United States, the prevalence of migraine is ≈ 12% and peaks in middle life (30-49 years of age), impacting patients in their prime working years.2,3 Approximately one-third of patients experience headache ≥ 4 days per month.4
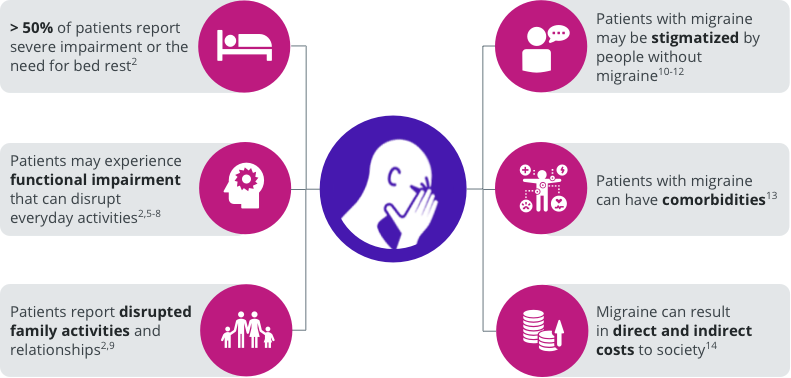
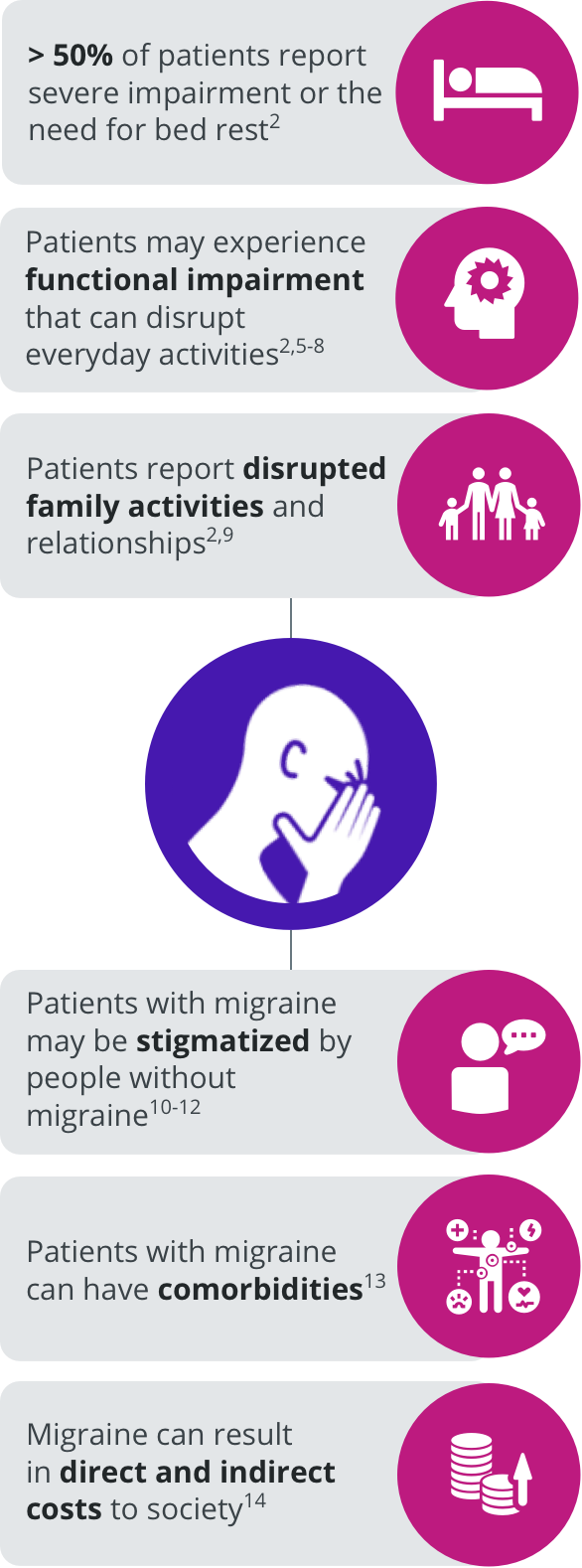
The burden of migraine can impact several domains of patients’ lives.2,5-14
TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE
Headache disorders, including migraine, are the second-leading cause of years lived with disability (YLD) globally among men and women.1 How does the frequency in migraine compare between the two in the United States?
A
B
C
D


Correct answer:
A
1. GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Lancet. 2018;392:1789-1858.
Clinical Phases of Migraine
Migraine can be divided into 5 phases.15-19 In addition to the characteristic moderate-to-severe head pain experienced during the ictal period, each of these phases may be associated with a range of non-headache symptoms.15-25
Phases of migraine and associated symptoms
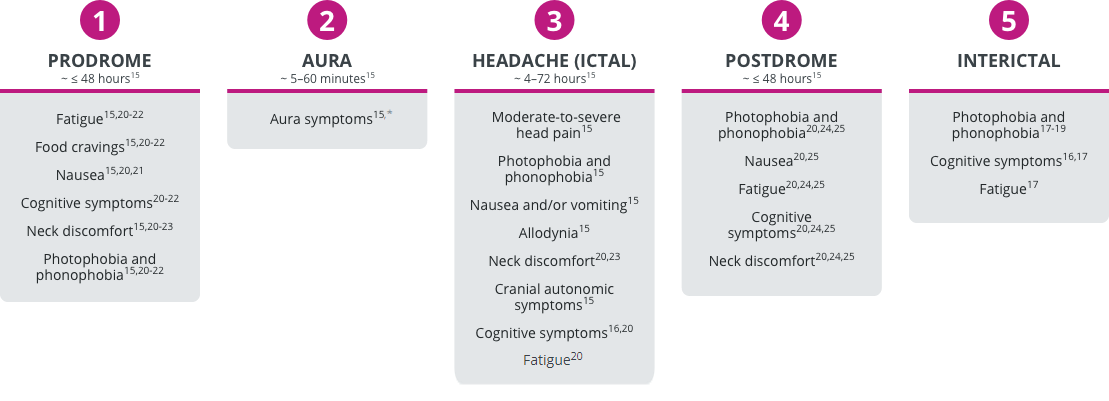

*Not all patients with migraine experience aura.15
Migraine has a complex pathophysiology that is becoming better understood.26 Recent studies have shown that several anatomic regions and molecular pathways underlie the multifaceted symptoms across all phases of migraine.27-30
TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE
When accounting for all phases of migraine, how long can a single migraine attack affect a patient?
A
B
C
D


Correct answer:
A
Migraine Severity and Disease Progression
Clinical findings suggest that migraine can progress over time.31,32 Approximately 3% of patients with migraine transition from episodic migraine (< 15 headache days per month) to chronic migraine (≥ 15 headache days per month for > 3 months, with features of migraine ≥ 8 days per month) every year.15,31,33 Conversely, one study showed that over a 2 year period, 26% of patients with chronic migraine transitioned back to episodic migraine.34 Several factors have been associated with this progression, including the presence of cutaneous allodynia, the presence of nausea, and the effectiveness of acute medication, with less optimal responses increasing the likelihood of a patient’s disease progressing over time.35,36
Migraine can be treated with both acute and preventive therapies, and patients who experience frequent attacks (≥ 4 headache days per month) may require a multidisciplinary approach, which may include a combination of acute and preventive modalities as well as behavioral interventions as part of their treatment plan.33,37
Migraine may have long-term clinical and pathophysiologic consequences for patients, including medication overuse headache (MOH) and neurologic sequelae.15,31,38,39
Migraine may have long-term clinical and pathophysiologic consequences for patients, including medication overuse headache (MOH) and neurologic sequelae.15,31,37,38
TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE
Which of the following symptoms may patients with migraine
report during their
headaches, as well as
in the days before and
after? Select all that apply.
A
B
C
D
E


Correct answer:
A, B, C, D, E



