Individual headache scores following CGRP infusion vs placebo
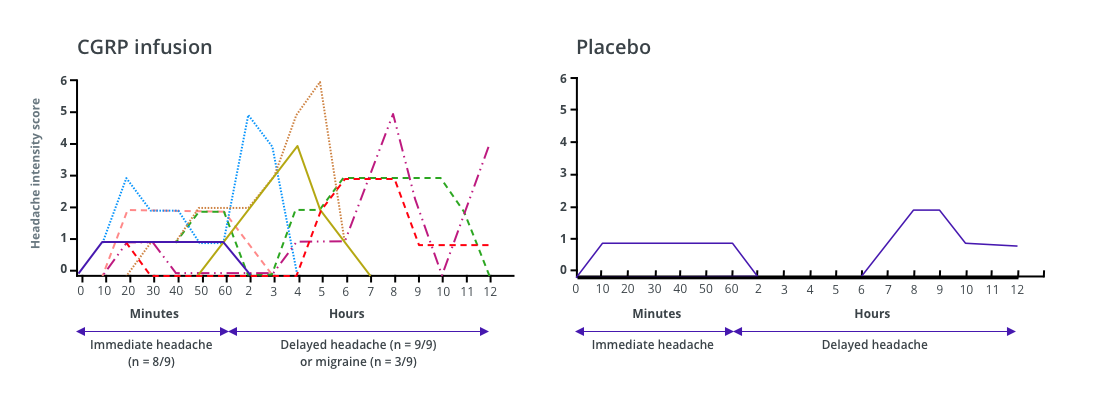
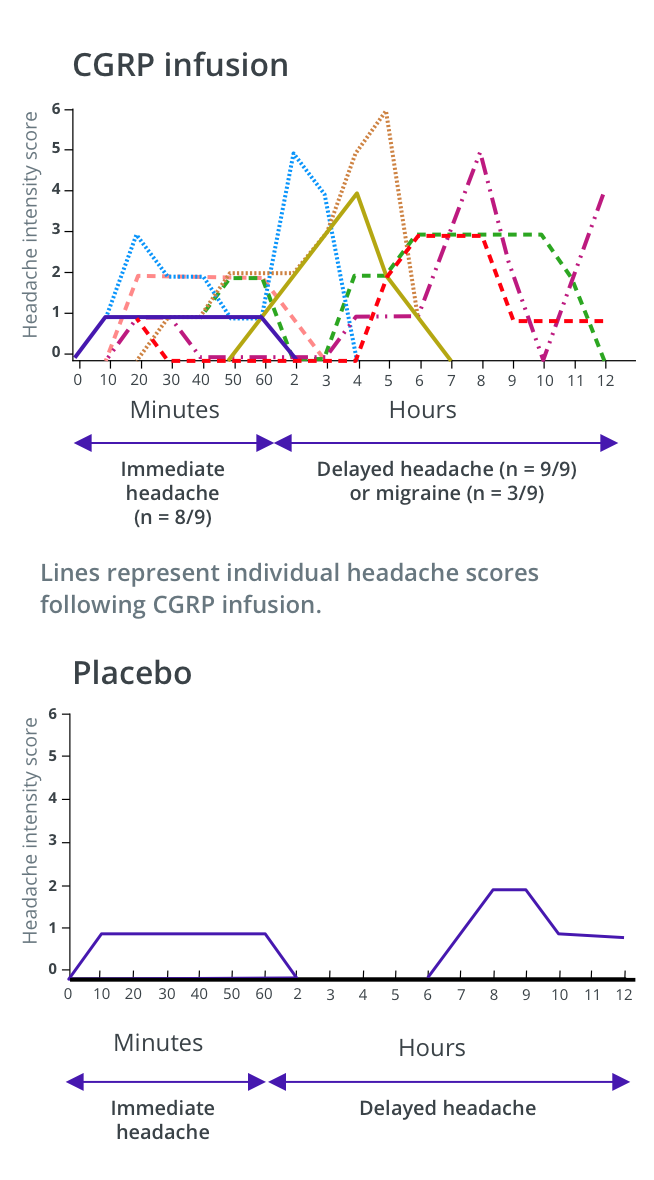
Lines represent individual headache scores following CGRP infusion
Individual headache scores after CGRP infusion, during the first 60 minutes after (immediate headache) and in the subsequent 11 hours (delayed headache) vs placebo.
Lanssen LH, et al. Cephalalgia. 2002;22:54-61, copyright © 2002 by SAGE Publications. Reprinted by permission of SAGE Publications, Ltd.
TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE
What clinical evidence supports the role of CGRP in migraine pathophysiology? Select all that apply.
A
B
C
D


Correct answer:
A, B
CGRP, calcitonin gene-related peptide.
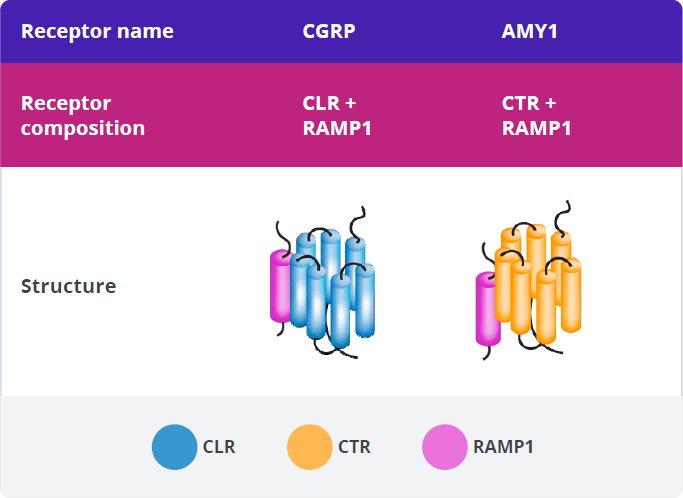
CGRP Receptor (CGRP-R)
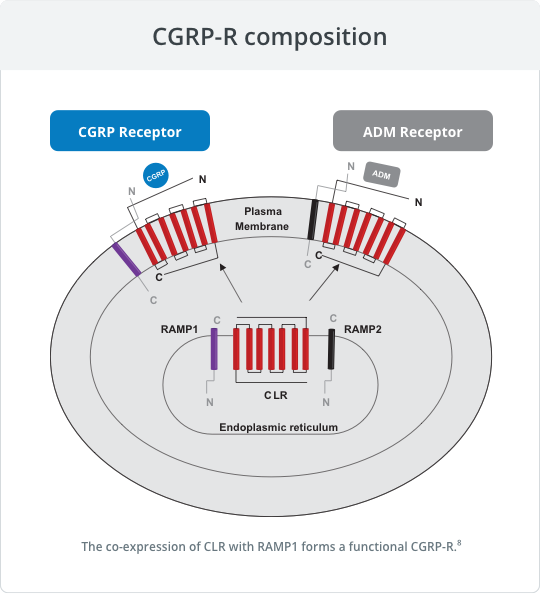
The calcitonin family of peptides binds transmembrane-bound, G-protein receptors that share subunits in different configurations. These are referred to as the calcitonin family of receptors. The CGRP receptor (CGRP-R) is a member of the calcitonin family of receptors.2
Each receptor is a heterodimer consisting of a receptor activity-modifying protein (RAMP) and either the calcitonin receptor (CTR) or calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CLR) G-protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling subunit.2
Calcitonin family of receptors
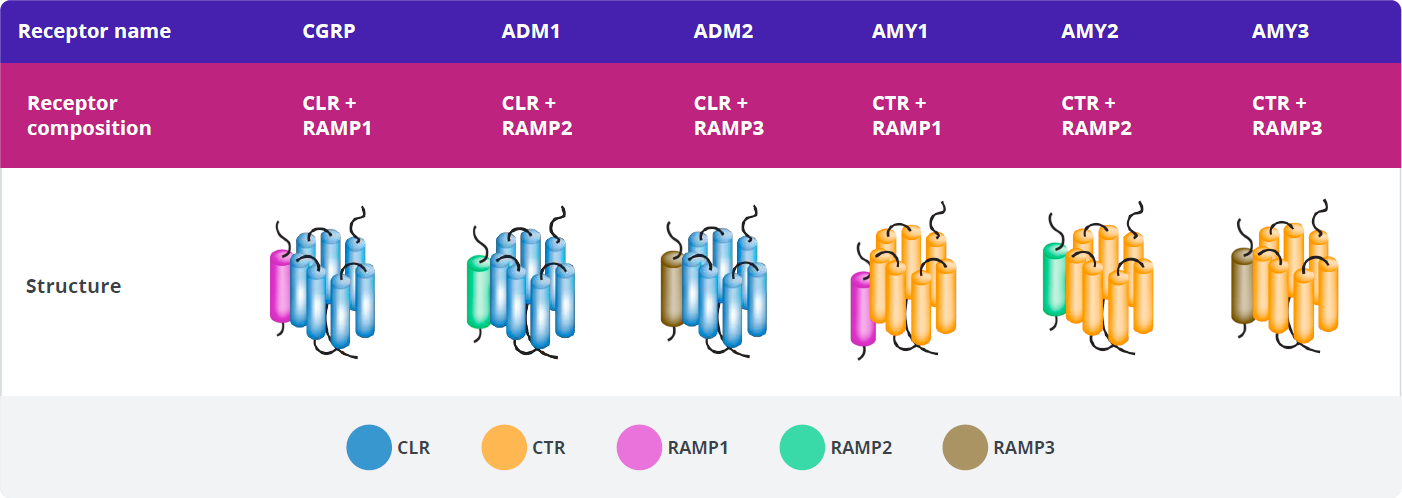
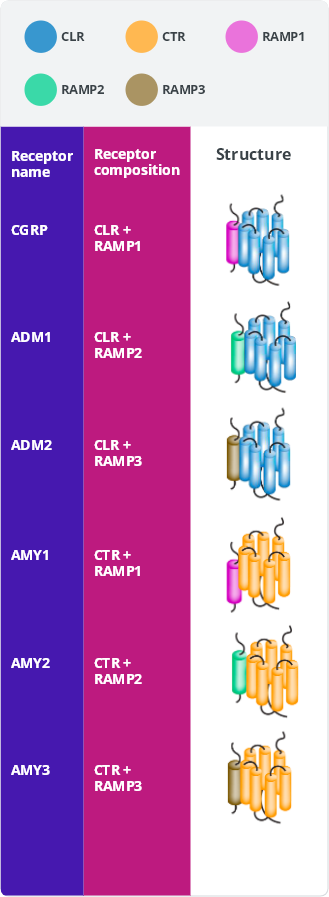
ADM, adrenomedullin; AMY, amylin; CGRP, calcitonin gene-related peptide
Association of CLR + RAMP1 yields the functional CGRP-R.2
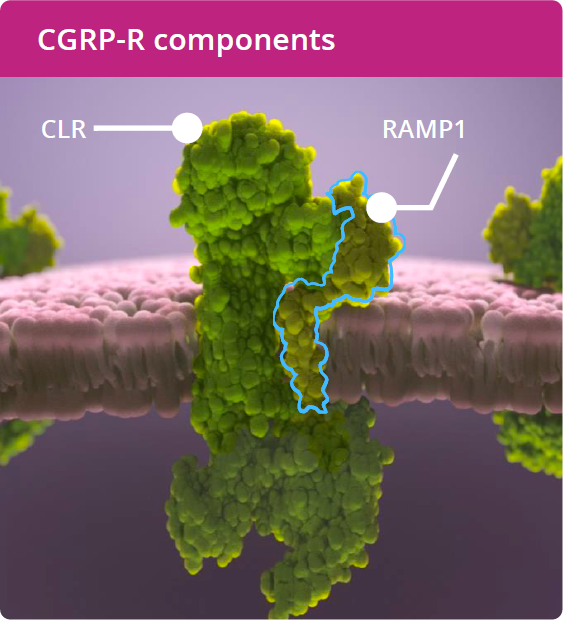
The CGRP-R is a membrane‐bound, G-protein–coupled receptor that comprises 2 subunits: CLR and RAMP1.1
Creation of a functional CGRP-R requires the co-expression of both CLR and RAMP1 and the formation of a heterodimer, which translocates from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell membrane.8-11
Activation of G-protein–coupled receptors involves a cyclical model, whereby receptors can be recycled back to the cell surface.12,13 Ligand binding leads to transient receptor activation and induces a cellular response via second-messenger signaling.12,13 Receptors are then inactivated and internalized via endocytosis before being trafficked to either recycling or degradative pathways.8,12-14
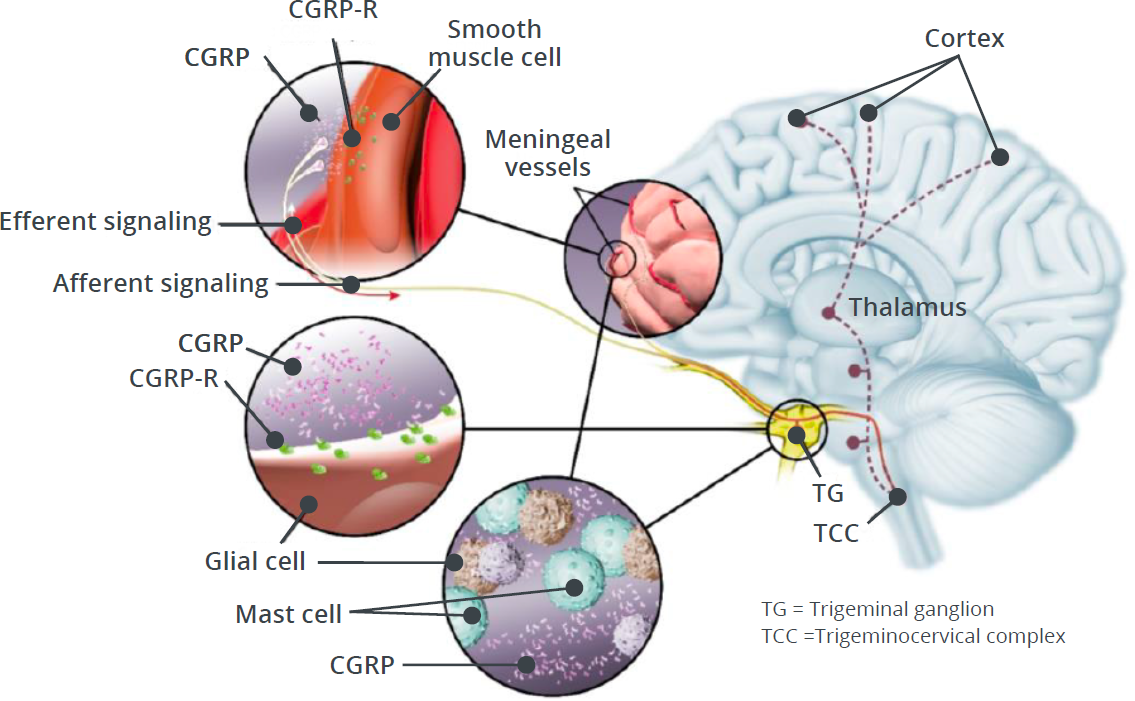
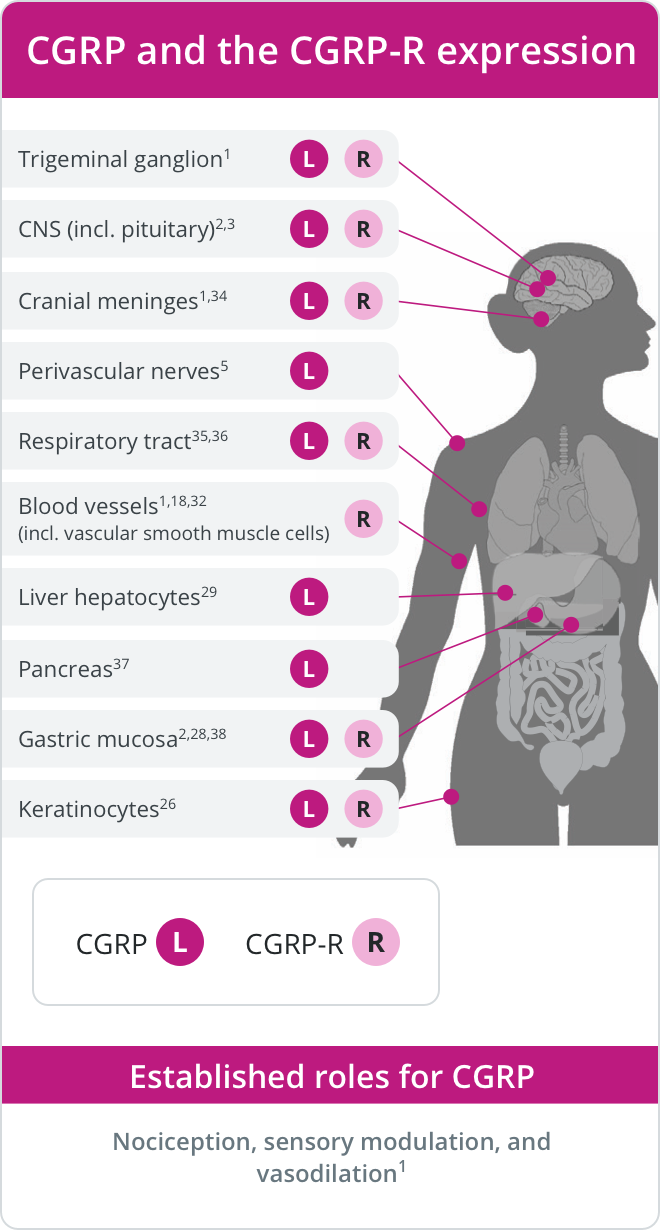
CGRP and CGRP-R Localization
CGRP-Rs are found in multiple areas involved in migraine pathophysiology, including:15-17
- Trigeminal ganglion
- Cerebral and meningeal vasculature
- Brainstem (eg, trigeminal nucleus caudalis)
- Brain (eg, thalamus)
CGRP-Rs are also expressed on numerous cell types, such as:15-19
- Vascular smooth muscle cells
- Neurons
- Glial cells
- Mast cells
Localization of CGRP and CGRP-R in migraine pathophysiology

![]()
CGRP and CGRP-R Signaling
Activation of CGRP-R in the trigeminovascular system plays a critical role in peripheral and central events that ultimately lead to the experience of migraine pain.15,20,21
Following nerve stimulation, CGRP is released from its storage vesicles through the process of calcium-dependent exocytosis.1
This peripheral release of CGRP from trigeminal nerve endings is thought to trigger multiple responses induced by CGRP-R binding, which eventually lead to the sensitization of nociceptor trigeminal neurons.15,20
The stimulation of peripheral nociceptive trigeminal neurons is hypothesized to relay the migraine pain signal through the brainstem into the brain, ultimately leading to the experience of migraine pain.21,22
Central effects of CGRP may involve pain transmission through sensitization and activation of central processes (eg, feedback from a sensitized brain).20
The complex role of CGRP–CGRP-R signaling in migraine pathophysiology may involve multiple processes in both the central and peripheral nervous systems, including:
Vasodilation15,16,20,23,24

Nociceptor activation (peripheral)15,16,20,23,24

Neurogenic inflammation15,16,20,23,24
Cortical-spreading depression15,20,24
Central trigeminal sensory activation16,20,23
Central sensitization20,23
Hypothalamic dysfunction and descending control of brainstem structures20,25
Research has yet to determine which of these processes play a causal role in, or if they occur as a result of, or in parallel with, migraine. Additional processes may also be involved that are yet to be defined.15,20
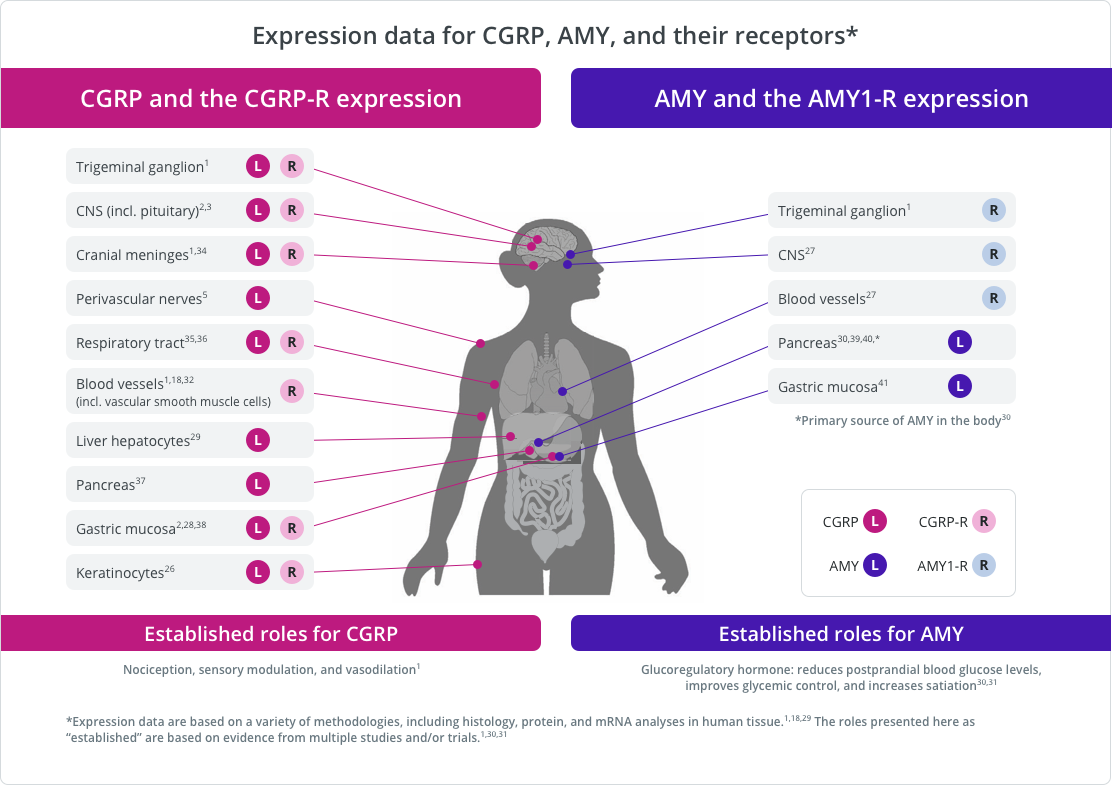
CGRP-R and AMY1-R Expression
In addition to binding to CGRP-R, CGRP has high affinity for another calcitonin receptor, the amylin 1 receptor (AMY1-R).2,3 These 2 receptors have the RAMP1 subunit in common.2

CGRP, amylin (AMY), and their receptors are expressed in various tissues and play established roles in some key physiologic processes.1,2,8,18,26-41 CGRP signaling through CGRP-R plays several firmly established physiologic roles, including nociception, sensory modulation, and vasodilation.1
The main source of amylin ligand is the pancreatic β-cells, and AMY1-R is expressed in the vasculature and the trigeminal ganglion.3,26–28
Various roles for AMY1-R have been suggested as a result of its location and the expression pattern of its ligands.4,26,27 Amylin signaling through AMY1-R plays well-established physiologic roles in regulating postprandial glucose levels, glycemic control, and satiation.26,27
Of the calcitonin receptors, only the CGRP receptor has been implicated in migraine pathophysiology.2 The roles of the other receptors in migraine pathophysiology are currently unknown.1,2
TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE
CGRP signaling is thought to play a role in migraine pathophysiology via which of the following mechanism(s)? Select all that apply.
A
B
C
D
E
F
G


Correct answer:
A, B, C, D, E, F, G
CGRP, calcitonin gene-related peptide.




